20058번: 마법사 상어와 파이어스톰
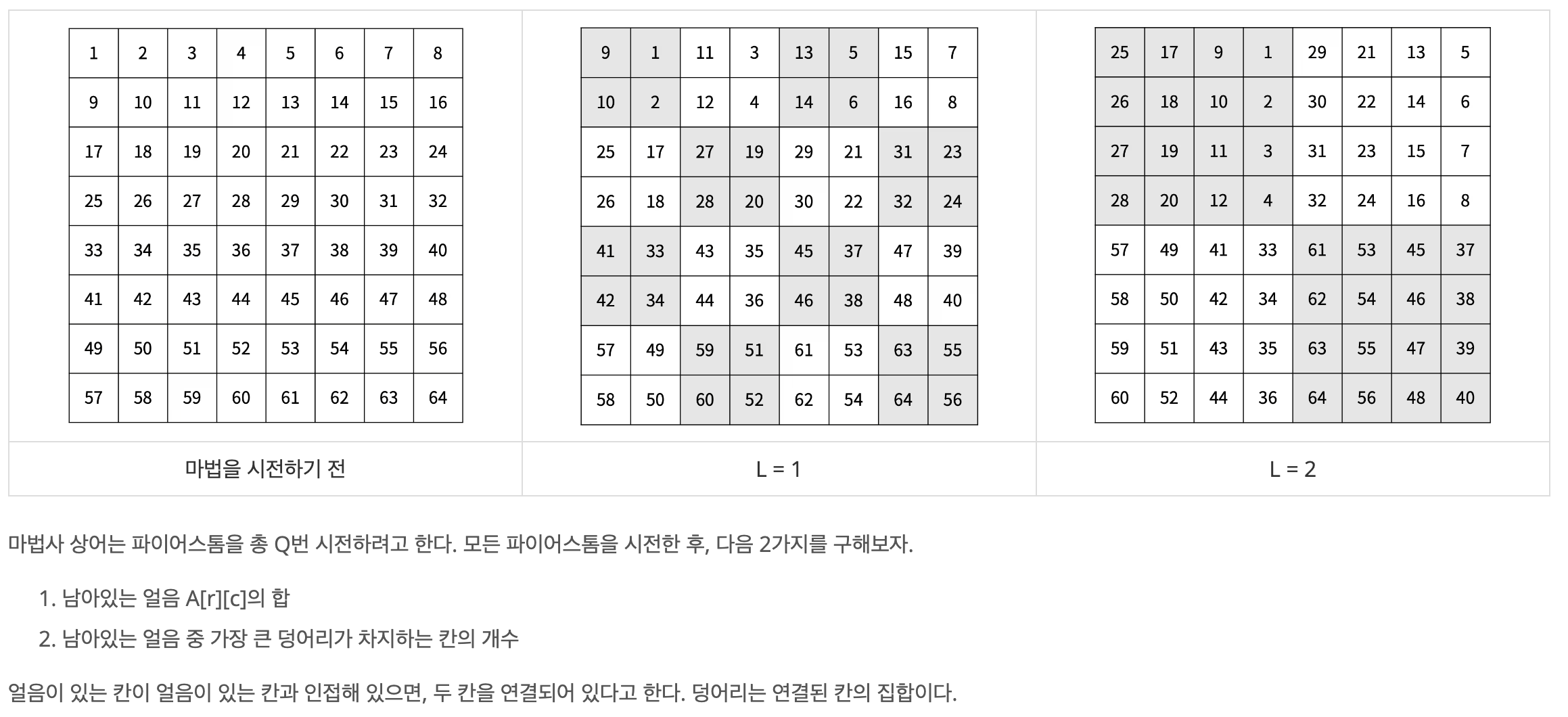
마법사 상어는 파이어볼과 토네이도를 조합해 파이어스톰을 시전할 수 있다. 오늘은 파이어스톰을 크기가 2N × 2N인 격자로 나누어진 얼음판에서 연습하려고 한다. 위치 (r, c)는 격자의 r행 c
www.acmicpc.net
import copy
from collections import deque
n, q = map(int,input().split())
area = [list(map(int,input().split())) for _ in range(2**n)]
visited = [[False]*len(area) for _ in range(len(area))]
l_list = list(map(int,input().split()))
dx = [0,0,-1,1]
dy = [-1,1,0,0]
total = 0
maximum = 0
def rotate90(i,j, area, n, new_area): # 오른쪽으로 90도 회전해서 저장하는 함수
for r in range(n):
for c in range(n):
new_area[i+c][j+n-1-r] = area[i+r][j+c]
def fire(n): # 단계 L에 따라 회전시킨 후 얼음을 녹이는 함수
global area
malt_list = []
new_area = [[0]*len(area) for _ in range(len(area))]
for i in range(0,len(area),2**n):
if i >= len(area):
break
for j in range(0,len(area),2**n):
if j >= len(area):
break
rotate90(i,j,area,2**n,new_area)
area = new_area
for i in range(len(area)):
for j in range(len(area)):
ice_count = 0
if area[i][j] == 0:
continue
for k in range(4):
temp_x, temp_y = i+dx[k], j + dy[k]
if 0 <= temp_x < len(area) and 0 <= temp_y < len(area) and area[temp_x][temp_y] > 0:
ice_count += 1
if ice_count < 3 and area[i][j] > 0:
malt_list.append((i,j))
for x, y in malt_list:
area[x][y] -= 1
def bfs(x,y): # (x,y) 좌표에 연결된 얼음 덩어리 면적을 반환하는 함수
if area[x][y] == 0 or visited[x][y]:
return -1
count = 0
queue = deque([(x,y)])
visited[x][y] = True
while queue:
current_x, current_y = queue.popleft()
count += 1
for i in range(4):
next_x, next_y = current_x+dx[i], current_y+dy[i]
if 0 <= next_x < len(area) and 0 <= next_y < len(area) and area[next_x][next_y] > 0 and not visited[next_x][next_y]:
queue.append((next_x,next_y))
visited[next_x][next_y] = True
return count
for l in l_list:
fire(l)
for i in range(len(area)):
for j in range(len(area)):
total += area[i][j]
temp_count = bfs(i,j)
if temp_count > maximum:
maximum = temp_count
for i in area:
print(i)
print(total)
print(maximum)
이번 문제는 주어진 2^N * 2^N 크기의 격자를 2^L * 2^L 크기의 격자로 나눠 각각 오른쪽으로 90도 회전시킨 후, 인접한 얼음이 3개 미만인 경우에는 얼음의 양이 1씩 줄어들도록 했을 때 최종적인 결과를 구하는 구현 문제이다.
먼저 2차원 배열의 값을 격자 크기(n)에 맞춰 회전하여 새로운 격자(new_area)에 저장하는 함수 rotate90() 함수을 구현하였고, 그 다음으로 단계(L)에 맞춰 모든 좌표를 회전시키고 조건에 맞는 얼음의 양을 줄여주는 fire() 함수를 구현하였다.
마지막으로 최종적인 격자에서 각 얼음 덩어리의 면적을 구하기 위해 BFS 함수를 사용하였다.
위 문제를 풀다보니 다음과 같은 2가지 문제와 개선점들을 찾을 수 있었다.
- 시뮬레이션 문제에서는 특정 조건을 기반으로 배열의 값을 수정하거나 반영하기 위해서는 "동시다발적"으로 처리해야 한다.(순서대로 처리하게 되면 앞의 값 수정이 다른 값들에게 영향을 줄 수 있음)
- copy.deepcopy() 함수로 2차원 배열을 복사하는 것은 많은 비용을 발생시키기 때문에 사용을 최대한 지양하여야 한다.
'Algorithm 💡 > Implementation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [프로그래머스] 안전지대 (0) | 2024.06.09 |
|---|---|
| [백준 23289번] 온풍기 안녕! (0) | 2024.04.13 |
| [백준 1388번] 바닥 장식 (0) | 2024.03.04 |
| [백준 14719번] 빗물 (0) | 2024.01.15 |
| [백준 20291번] 파일 정리 (0) | 2024.01.06 |



